Data privacy compliance didn’t emerge overnight. It’s a response to the dramatic rise in the value of data, which began in the mid-1900s when companies and corporations started actively collecting, storing, and sorting people’s information (e.g., mailing lists, banking details).
With the rise of the internet, the focus was initially on “security” rather than “privacy.” However, this changed when companies like Google started leveraging user data to improve search results and advertising. Social media platforms further fueled this model, leading to sophisticated data-driven algorithms predicting consumer behavior.
In 2018, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) went into effect, causing major changes in how companies handle personal data. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in 2019 marked the first modern privacy legislation in the United States, followed by other states considering similar laws.
“By year-end 2024, Gartner predicts that 75% of the world’s population will have its personal data covered under modern privacy regulations,” said Nader Henein, VP Analyst at Gartner.
This underscores the global shift towards a more privacy-conscious society. Businesses must adapt and evolve, recognizing that data privacy protection is no longer a mere legal requirement but a fundamental aspect of building customer trust.
With the right approach, compliance will become a seamless part of your business operations. Let’s explore some essential strategies to make data privacy compliance more achievable.
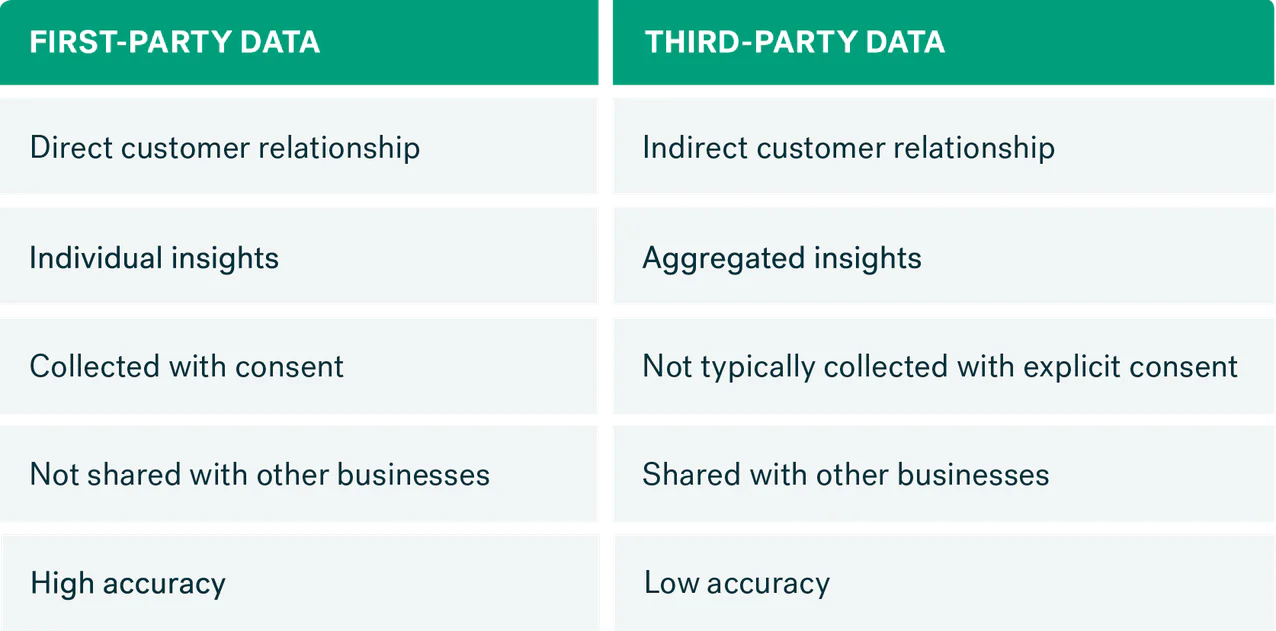
Unlike third-party data acquired from external sources, first-party data is gathered through direct interactions such as purchase history, website analytics, and customer support interactions. Recently, there’s also been an emphasis on zero-party data, or the data that customers explicitly provide your business (e.g., filling out a form or survey).
Because zero- and first-party data is sourced directly, it’s the most accurate and relevant data you can have, which allows for enhanced personalization and better decision-making. It also aligns well with data privacy laws to minimize the risk of legal issues.
Here’s how to start focusing on collecting, managing, and using zero- and first-party data:
Gather data through your own channels: Use website forms, mobile apps, and customer support interactions to collect valuable insights about your customers.
Engage with surveys and feedback: Encourage customers to participate in surveys and provide incentives for feedback to enrich your first-party data set.
Implement a customer data platform (CDP): A CDP unifies data from various sources into a centralized hub to improve accessibility and management for your team.